Catheterize the central vein (subclavian or jugular) and measure central venous pressure (CVP).
| № | Critical violations | ECG and coronary readings | EChOKG changes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
Acute coronary syndrome with ST-segment elevation and coronary syndrome without ST-segment elevation |
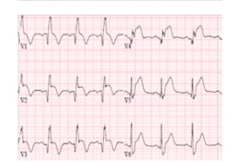
|
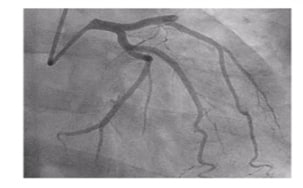
|
| 2 |
Acute myocardial injury without vascular atherosclerosis a) myocarditis b)stress cardiomyopathy |
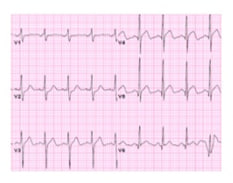
|
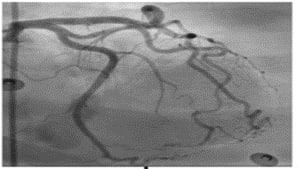
|
| 3 | Arrhythmias |
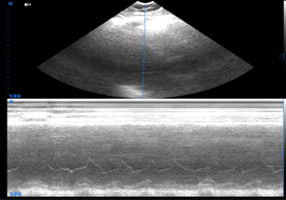
|
|
| 4 | Heart failure |
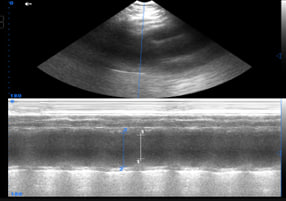
|
|
| 5 | Pericardial effusion |

|
|
| 6 | Thromboembolic complications |
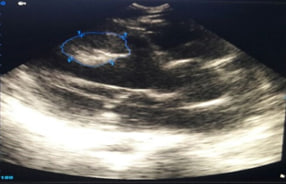
|